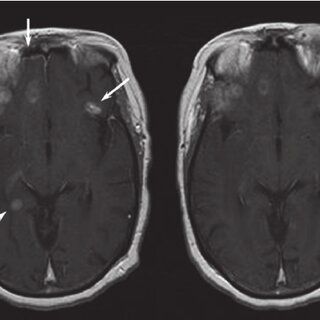
Brain tumors, while rare, require early and accurate detection to guide effective patient care. Neuroradiology, a specialized field within radiology, plays a role in identifying and understanding these complex conditions. By using cutting-edge imaging techniques, neuroradiologists provide the detailed brain studies necessary for diagnosis, treatment planning, and ongoing patient monitoring. For medical students and radiology technicians exploring this field, this article offers insight into how neuroradiology contributes to detecting brain tumors.
Neuroradiology
Using advanced technologies, neuroradiology focuses on imaging the brain, spine, and nervous system. It gives clinicians a detailed look inside the brain to assess abnormalities, injuries, or suspected tumors. Advanced tools, such as MRI, CT scans, and PET scans, allow neuroradiologists to visualize the brain’s intricate structure with remarkable clarity.
With its ability to identify subtle changes in brain tissue, neuroradiology is keyk when doctors suspect a brain tumor. These imaging methods help map the tumor’s location, size, and effect on surrounding brain structures while minimizing invasive procedures. Understanding these key components in moving toward precise patient care.
Key Imaging Techniques in Neuroradiology
Neuroradiology employs several imaging techniques, each offering distinct insights into the brain’s structure and function. These imaging techniques work together to create a clearer picture of the brain, assisting neuroradiologists in identifying brain tumors with precision.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create highly detailed images of the brain. It is particularly useful for detecting soft tissue abnormalities, such as tumors.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scans: CT scans combine X-rays and computer technology to provide cross-sectional images, often used as a first-line imaging method for suspected brain tumors.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scans: PET scans focus on metabolic activity in brain tissues, offering insight into whether a tumor is likely malignant or benign.
The Role of Contrast Media in Brain Tumor Detection
Contrast media, used in neuroimaging, significantly enhances the detection and differentiation of brain tumors. Many imaging techniques, including MRIs and CT scans, incorporate these substances to provide clearer images. Tumors tend to disrupt the blood-brain barrier, causing the contrast to pool in abnormal areas. Neuroradiologists analyze these patterns to determine the tumor’s borders and complexity. This additional level of precision greatly aids in creating personalized treatment strategies.
The Challenges Faced in Neuroradiology
While neuroradiology offers invaluable support in detecting brain tumors, professionals in this field face several challenges. Conducting detailed imaging may require patients to remain still for long periods, which can be difficult for some individuals. Medical advancements are actively addressing these concerns with improved imaging speed and patient comfort.
Another challenge is interpreting ambiguous imaging results. Certain types of tumors, such as low-grade gliomas, can be challenging to differentiate from non-cancerous abnormalities. Neuroradiologists rely on extensive expertise to minimize misinterpretation, so that patients receive highly accurate diagnoses.
Why Neuroradiology Matters
The role of neuroradiology in brain tumor diagnostics extends beyond merely identifying abnormalities. By providing imaging data, neuroradiologists allow healthcare teams to plan treatments tailored to their patient’s needs. These imaging tools also facilitate the monitoring of treatment effectiveness and potential tumor recurrence.
Taking The Next Steps Foward
Neuroradiology is an indispensable part of detecting and diagnosing brain tumors. By combining advanced imaging techniques, contrast analysis, and professional expertise, neuroradiologists contribute significantly to patient care. Whether you’re a medical student exploring potential specialties or a radiology technician honing your skills, understanding this field highlights its profound impact on healthcare. For those looking to broaden their expertise, look into further exploring neuroradiology’s diagnostic tools and methodologies.
Also read: Golang vs Other Languages