Have you ever wondered how contaminants in water are removed to make it safe for drinking? With growing concerns about pollution, the need for effective water treatment methods is more urgent than ever. One of the most dangerous contaminants gaining attention today is PFAS. But how can people tackle such long-lasting pollutants?
Activated carbon is one of the most productive methods for tackling PFAS and similar contaminants. This robust filtration material has become a key player in the effort to clean water and protect public health. But how exactly does it work, and why is it critical to address contamination issues?
How It Works in Filtration
Activated carbon is a highly porous material that can trap contaminants, including PFAS, through a process known as adsorption. In this process, pollutants’ molecules are attracted to the material’s surface and bind to it, effectively removing them from the water.
This filtration method is effective because it can target various contaminants, from volatile organic compounds to harmful chemicals. Its versatility allows it to be used in multiple filtration systems, ensuring cleaner water for homes and industries.
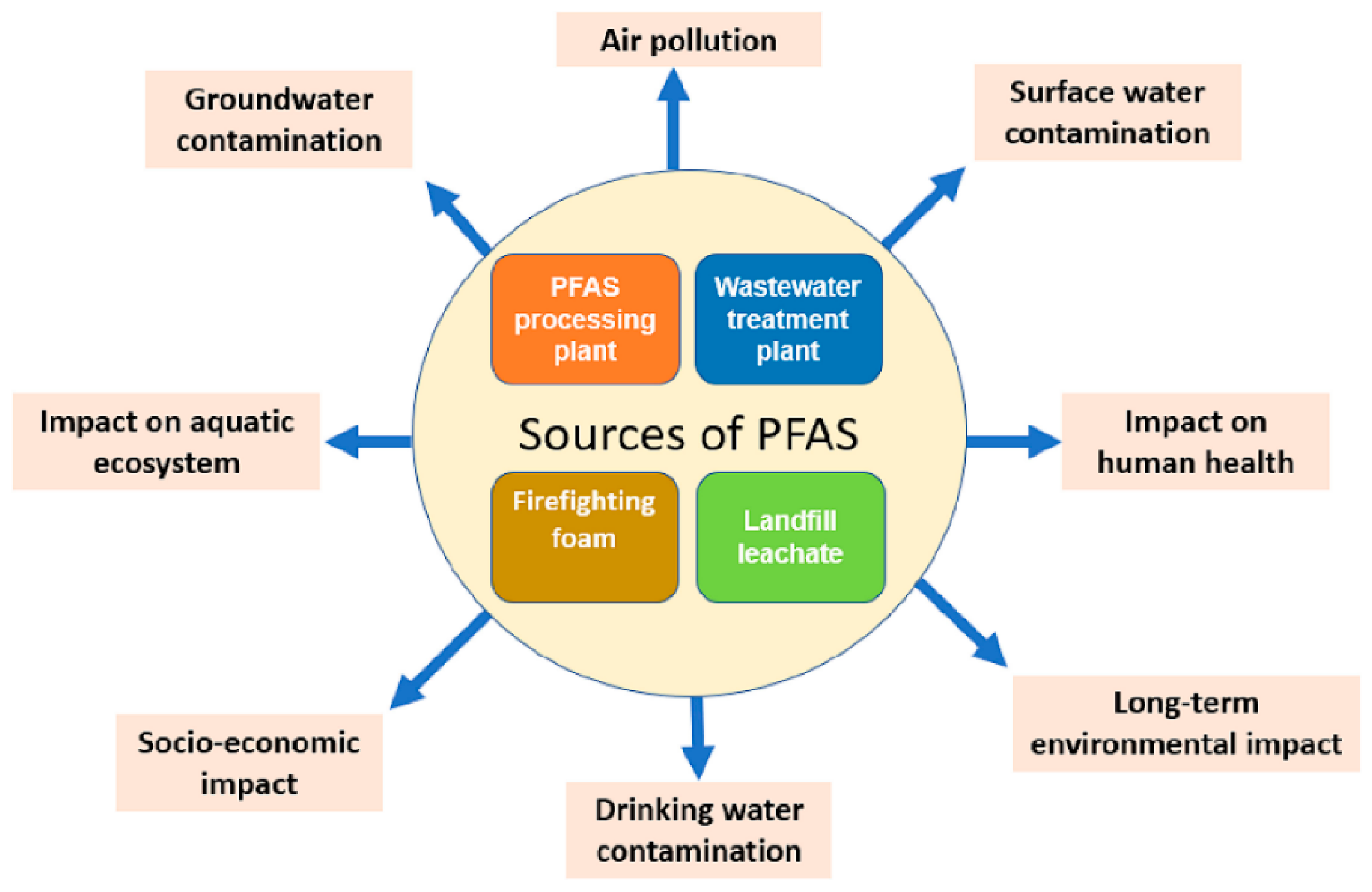
PFAS: A Growing Environmental Concern
PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of artificial chemicals used in various industrial applications. Unfortunately, these compounds do not break down easily in the environment, leading to their accumulation in sources. Long-term exposure to PFAS has been linked to various health concerns, including cancer, liver damage, and immune system disorders.
Removing them from the supply has become a priority for many municipalities, and this is where carbon filtration comes into play. The material can trap and hold PFAS, preventing them from entering drinking water systems.
Versatility in Tackling Other Contaminants
While PFAS is a significant concern, it’s not the only pollutant that carbon filtration can handle. It’s also effective against other harmful contaminants such as chlorine, pesticides, and heavy metals. This makes it a comprehensive solution for improving quality.
Whether used in large-scale water treatment plants or smaller household filters, this material can provide cleaner, safer water. Its adaptability ensures that it can tackle various contamination challenges across different settings.
Environmental Impact of Effective Filtration
Carbon filtration improves water quality and has a positive environmental impact. By removing harmful chemicals from water before they are released back into nature, the material helps protect aquatic ecosystems.
This can prevent the contamination of rivers, lakes, and oceans, essential to maintaining biodiversity and preserving the planet’s health. The long-term benefits of effective filtration systems extend beyond human health, safeguarding wildlife and ecosystems from dangerous pollutants.
Cost-Effective and Reliable Solution
One reason carbon filtration as well as reverse osmosis has become so widely used is its cost-effectiveness. Compared to other purification methods, such as advanced chemical treatments, it offers an affordable option for consumers and industries.
Its longevity and effectiveness make it a reliable choice for ensuring clean water. Once the filtration system is installed, it requires minimal maintenance, reducing the need for expensive upgrades or constant replacements.
Challenges in Maintaining Clean Water
While carbon filtration is a powerful tool in tackling contaminants, maintaining clean water is an ongoing challenge. Emerging contaminants like PFAS require continuous monitoring and innovation in filtration technology.
The key is to adapt these systems as new pollutants are discovered and to ensure that filtration materials remain effective over time. Regular replacement and maintenance of these systems are crucial for their continued efficiency.
Activated carbon is critical in addressing contamination issues like PFAS and other harmful substances in water. This highly effective filtration material provides a reliable and cost-efficient solution to the growing water pollution problem. As environmental concerns persist, the need for advanced filtration methods will only grow.